Title Tag
What is a Title Tag?
A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. A page’s title tag is displayed as part of the search snippet in a search engine results page (SERP). It appears as the clickable headline for the search result and is important for user experience, SEO, and social sharing. The title tag of a web page is meant to be an accurate and concise description of a page's content.
Need help writing perfect title tags for your website? Use our free Title Tag Preview Tool by entering your title tag text below to see how it's likely to appear in Google's search results:
For the most accurate results, view on a desktop browser.
Note: You may also see title tags referred to as "meta titles" or "meta title tags" in some cases. While controversial with some, either usage is typically fine.
Title Tag Examples
HTML code example
<head><title>Example Title</title></head>
You can find your page’s title tag within the <head> section of the page’s HTML markup.

Most CMSs will allow you to edit this markup and change your title tag either directly within the code or via the title tag field within the page’s metadata settings.
Format example
Primary Keyword - Secondary Keyword | Brand Name
8-foot Green Widgets - Widgets & Tools | Widget World
Optimal title tag length
While Google does not specify a recommended length for title tags, most desktop and mobile browsers are able to display the first 50–60 characters of a title tag. If you keep your titles under 60 characters, our research suggests that you can expect about 90% of your titles to display properly in the SERPs. (There's no exact character limit because characters can vary in pixel width. Google SERPs can usually display up to 600 pixels.) While writing concise titles is important for human readability and comprehension, Google’s spiders will take into account the entire title tag (within reason) when they crawl the page, even if it is not displayed in full in the SERPs.
Use Page Optimization in Moz Pro for better title tags
Moz Pro's Page Optimization feature can help you identify pages whose rankings could benefit from improved title tags. Take a 30-day free trial on us and see what you can achieve:
Why are title tags important?
Title tags are major factors in helping search engines understand what your page is about, and they are the first impressions many people get when they discover your page via organic search. Title tags are used in three key places: (1) search engine results pages (SERPs), (2) web browsers, and (3) social networks.
1. Title tags in SERPs
Your title tag determines your display title in SERPs (with a few exceptions) and is a search visitor's first experience with your site. Even if your page ranks well, a good title can be the make-or-break factor in determining whether or not someone clicks on your link.

2. Title tags in web browsers
When someone visits your page, the title tag is also displayed at the top of their web browser window and acts as a placeholder, especially when there are several browser tabs open. Unique and easily recognizable titles with important keywords near the front help ensure that people don't lose track of your content.
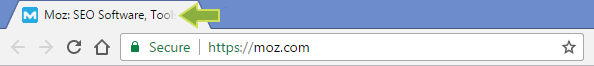
3. Title tags on social networks
Some external websites — especially social networks — will use your title tag to determine what to display when the page is shared. Here's a screenshot from Facebook, for example:

Keep in mind that some social networks (including Facebook and Twitter) have their own meta tags, allowing you to specify titles that differ from the HTML title tag that's marked up in your page's code. This can allow you to optimize for each network and provide longer titles when/where they might be beneficial.
How do I write a good title tag?
Because title tags are such important parts of both search engine optimization and the search user experience, writing them effectively is a terrific low-effort, high-impact SEO task. Here are some critical recommendations for optimizing title tags for search engine and usability goals:
1. Watch your title length
If your title is too long, search engines may change your display title by adding an ellipsis ("..."), removing words, or even rewriting it entirely. While we generally recommend keeping your titles under 60 characters long, the exact display limit is a bit more complicated and is based on a 600-pixel container.
Some characters naturally take up more space. A character like uppercase "W" is wider than a lowercase character like "i" or "t". Take a look at the examples below:

The first title displays a full 77 characters because the "ittl" in "Littlest" is very narrow, and the title contains pipes ("|"). The second title cuts off after only 42 characters because of wide capital letters (like "W") and the fact that the next word in the title tag (the part being cut off) is the full website name.
Try to avoid ALL CAPS titles. They may be hard for search visitors to read, and may severely limit the number of characters Google can display.
Keep in mind that, even within a reasonable length limit, search engines may choose to display a different title from what you provide within your HTML. For example, Google might append your brand name to the display title, like this:
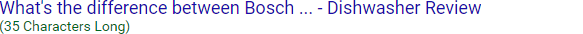
Here, because Google cut off the text before adding the brand name (the text before "..." is the original text), only 35 characters of the original title were displayed. See more below about how to prevent search engines from rewriting your title tags.
Keep in mind that longer titles may work better for social sharing in some cases, and some titles are just naturally long. It's good to be mindful of how your titles appear in search results, but there isn't a penalty for using a long title. Use your judgment and think like a search visitor.
2. Don't overdo your keywords
While you won't be penalized for a long title, you can run into trouble if you start stuffing your title full of keywords in a way that creates a bad user experience, as in this example:
Buy Widgets | Best Widgets | Cheap Widgets | Widgets for Sale
Avoid titles that are just a list of keyword phrases or variations of the same keyword over and over. These titles are bad for search users and could get you into trouble with search engines. Search engines are becoming better than ever at understanding variations of keywords, and it's unnecessary and counterproductive to stuff every version of your keyword into a title.
3. Give every page a unique title
Unique titles help search engines understand that the content on a page is uniquely valuable, and they also drive higher click-through rates. On a scale of hundreds or thousands of pages, it may seem impossible to craft a unique title for every page, but modern CMS and code-based templates should allow you to at least create data-driven, unique titles for almost every important page of your site. For example, if you have thousands of product pages with a database of product names and categories, you could use that data to easily generate titles like:
[Product Name] - [Product Category] - [Brand Name]
Absolutely avoid default titles, like "Home" or "New Page" — these titles may cause Google to think that you have duplicate content across your site (or even across other sites on the web). In addition, these titles almost always reduce click-through rates. Ask yourself: How likely would you be to click on a link from the SERP that says "Untitled" or "Product Page"?
4. Put important keywords first
According to Moz's testing and experience, keywords closer to the beginning of your title tag may have more impact on search rankings. In addition, user experience research shows that people may scan as few as the first two words of a headline. This is why we recommend titles where the most unique aspect of the page (e.g. the product name) appears first. Avoid titles like:
Brand Name | Major Product Category | Minor Product Category | Name of Product
Titles like this example front-load repetitive information and provide very little unique value at first glance. In addition, if search engines cut off a title like this, the most unique portion is the most likely to disappear. These titles may also appear keyword-loaded and are likely to be rewritten by Google.
5. Take advantage of your brand
If you have a strong, well-known brand, adding it to your titles may help boost click-through rates. We generally still recommend putting your brand at the end of the title, but there are cases (such as for your home page or about page) where you may want to be more brand-focused. As mentioned earlier, Google or your CMS may also append your brand name to your display titles automatically, so be mindful of how your search results are currently displayed.
6. Write for your customers
While title tags are very important to SEO, remember that your first job is to attract clicks from well-targeted visitors who are likely to find your content valuable. It's vital to think about the entire user experience when you're creating your title tags, in addition to optimization and keyword usage. The title tag is a new visitor's first interaction with your brand via organic search — it should convey the most positive and accurate message possible.
Why won't Google use my title tag?
Sometimes, Google may display a title that doesn't match what you've marked up in your HTML. This can be frustrating, but there's no easy way to force the search engine to use the title you've defined. When this happens, there are three likely explanations:
1. Your title is keyword-stuffed
As discussed above, if you try to stuff your title with keywords (sometimes called "over-optimization"), Google may choose to simply rewrite it. Google also seems to be sensitive to phrases patched together with delimiters, such as pipes (|). For this and many other reasons, consider tuning up your title to be more useful to search users.
2. Your title is too long
It used to be that Google would simply cut off a long title. While inconvenient at times, that was at least predictable! More recently, Google has begun completely rewriting long titles, taking a portion of the title from the middle or using other text on the page. While you shouldn’t panic over long titles, it’s important to be mindful of how those titles appear in SERPs.
3. Your title has relevance issues
We covered the obvious cases, like a page titled “Home,” but Google may rewrite any title that doesn’t seem to match searcher intent or that’s loaded with marketing jargon or phrases that don’t reflect the content. These rewrites aren’t restricted to keyword stuffing or obvious spam. Make sure your titles accurately reflect the corresponding content.
4. You have an alternate title
In some cases, if you include alternate title data, such as a meta tag for Facebook or Twitter, Google may choose to use that title instead. Again, this isn't necessarily a bad thing, but if this creates an undesirable display title, you might want to rewrite the alternate title data.
Keep learning
- The Beginner's Guide to SEO
- 9.5 Ways Google Rewrites Your Title Tags
- SEO Master Class: Advanced Title Tag Optimization (for Any Site) - Webinar
- 7 Title Tag Hacks for Increased Rankings + Traffic - Whiteboard Friday
- Title Tags SEO: When to Include Your Brand and/or Boilerplate
Put your skills to work
Improve your search engine visibility with Moz Pro
The complete SEO tracking and research toolset